Non-invasive real-time cerebral monitoring and blood flow-guided evaluation of early rehabilitation intervention after stroke.
Network project partners and key network researchers involved

Raquel Delgado-Mederos
Joan Martí-Fàbregas
Project summary
Stroke is the second leading cause of disability in Europe after ischemic heart disease and is the sixth leading cause worldwide. The prevalence of stroke events is expected to increase across the globe as the global population aged over 65 increases.
In acute ischemic stroke (AIS), i.e. the majority of strokes, early reperfusion of the obstructed artery, that is, restored cerebral blood flow (CBF), is a robust predictor of early recovery and favorable functional outcome.
Diffuse optical technology offers a new opportunity for non-invasive, real-time and bedside assessment of brain function biomarkers, including CBF, therefore aiming to provide an earlier prediction of response to therapy, leading to improved clinical decisions and outcomes.
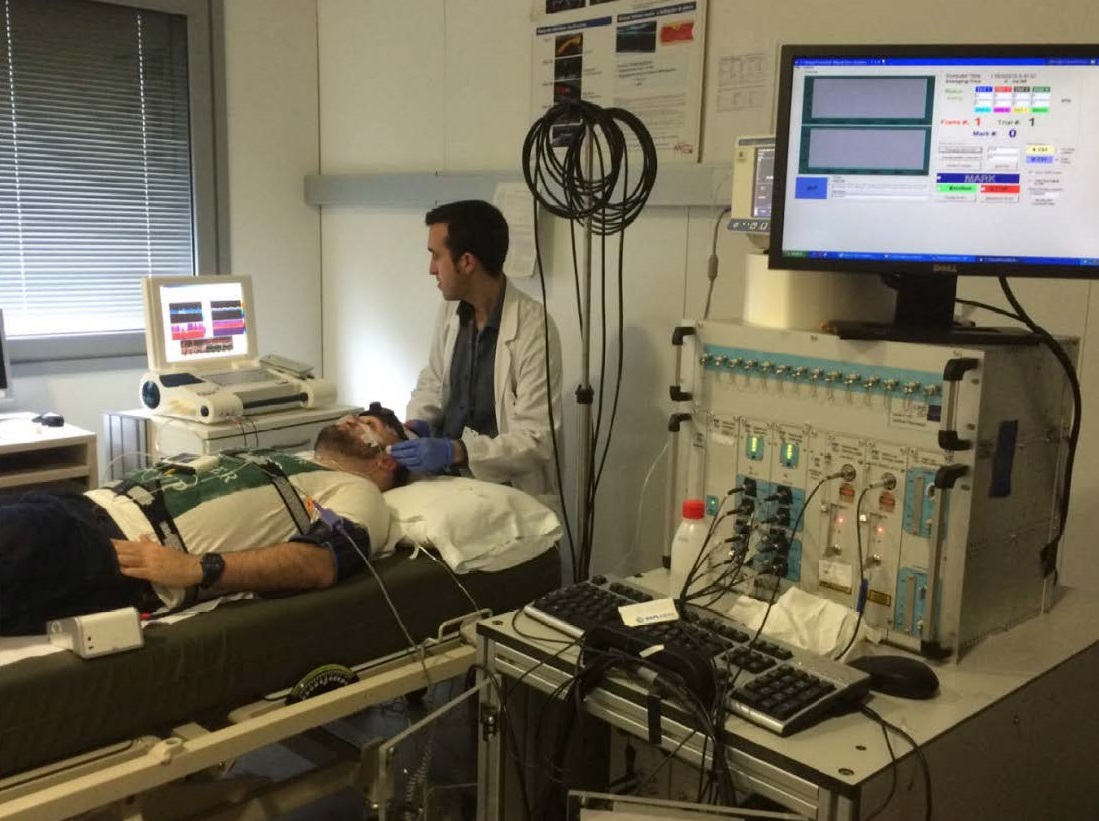
Researchers in the Medical Optics group led by ICREA Professor at ICFO Dr. Turgut Durduran are developing technologies using near infrared light and diffuse optical technologies to provide physicians with helpful information in a safe manner and at the bed-side of the patient.
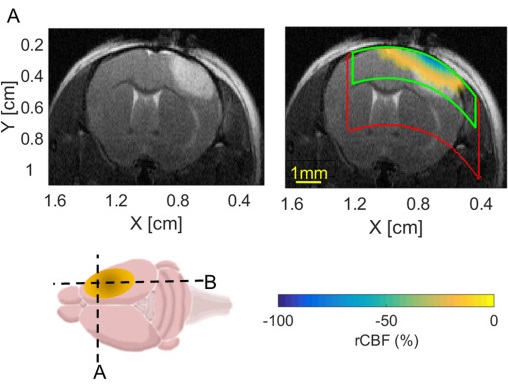
ICFO researchers team up with the Stroke Unit of Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau for clinical testing of these devices. They also team up with the Cerebrovascular Research Group at IDIBAPS to understand the fundamentals of ischemic stroke in animal models.
These photonic devices non-invasively monitor the tinniest vessels of patient’ brains, providing continuous information on blood-flow, blood volume, blood oxygenation and oxygen consumption. They are used to complement powerful tools like MRIs and CT-scans and aim to optimize treatments and improve outcomes and quality of life for stroke patients. The ultimate goal is to develop devices that can be widely used in all stroke units, expanding to portable devices for use in ambulances.
Highlighted publications
Blood flow response to orthostatic challenge identifies signatures of the failure of static cerebral autoregulation in patients with cerebrovascular disease
Early microvascular cerebral blood flow response to head-of-bed elevation is related to outcome in acute ischemic stroke
Microvascular cerebral blood flow fluctuations in association with apneas and hypopneas in acute ischemic stroke
High-density speckle contrast optical tomography (SCOT) for three dimensional tomographic imaging of the small animal brain
Funding institutions